- English (United States)
- 日本語
WG1:Elucidating the degradation mechanism due to salt damage and evaluating material properties and performance of structures
Staff introduction
- Chairman Shinichi Miyazato (Kanazawa Institute of Technology)
- Sadao Kimura (Kanazawa Institute of Technology)
- Mitsuharu Tokunaga (Kanazawa Institute of Technology)
- Shōji Takechi (Kanazawa Institute of Technology)
- Hajime Itō (Toyama Prefectural University)
- Yūya Sakai (University of Tokyo)
- Kōji Ishii (Kanazawa University Visiting Professor, P.S Mitsubishi Construction Co. Ltd.)
- Toshiyuki Aoyama (Kanazawa University Visiting Associate Professor, P.S Mitsubishi Construction Co. Ltd.)
- Minobu Aoyama (Central Nippon Highway Engineering Nagoya Company Limited)
- Yūichi Ishikawa (Central Nippon Highway Engineering Nagoya Company Limited)
- Shinya Kitagawa (Sato Kogyo Co.,Ltd.)
Overview
WG(1) explains the degradation mechanisms of the salt damage deterioration caused by salt penetration due to airborne salt and anti-freezing agents in coastal areas. Focusing on the superstructure, WG1 takes a role in studying structural heath evaluation criterion based on the correlation between the clarification of damage mechanisms of the previously deteriorated cases and the evaluation of loading capacity based on loading tests conducted on salt damage deteriorated girders of the real bridge.
①Fabrication of PC.JIS girder (from now on, testing PC girder) and acceleration of salt damage deterioration.
②Comparison of salt permeability between airborne salt and anti-freezing agent
③Creating a regional map of salt damage degradation bridges
④Experimental and analytical study on the effects of steel corrosion degree upon serviceability and load bearing capacity of RC-PC testing girders.
⑤Assessing the influence of complex deterioration due to “Salt damage and ASR” and “salt damage and neutralization” in ④
⑥-1 Evaluating steel corrosion degree based on loading tests and dismantling investigation of PC testing girders manufactured in ① and removal PC girders
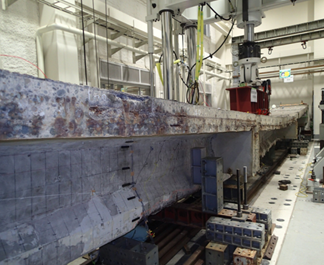

Photo 1 Loading test of PC girder deteriorated due to salt damage
⑥-2 Creating the evaluation criteria for visual inspection and judging degree of deterioration due to steel corrosion on the real bridges
⑦Measures to control salt damages based on the regional standardization of fly ash concrete
⑧New proposal of maintenance management system for salt damage degradation bridges
⑨Developing the monitoring technology using titanium wire

to measure the potential difference when the reinforcement bar
rusted
⑩Improving the inspection technology by the hammering method for RC desk slab bearing the deteriorated salt damage


